

Moths, along with butterflies, are part of the order Lepidoptera (from the Greek for scaled wings). Over 90% of New Zealand’s Lepidoptera species are endemic, found nowhere else in the world ...
READ MORE

Moths make up the third most diverse insect group in New Zealand, and their day/night habits are also diverse. While most moths are nocturnal (active at night), others are diurnal (active during ...
READ MORE

Moths are members of the order Lepidoptera, but these mostly nocturnal creatures are often in the shadow of the brighter, day-flying butterflies. New Zealand has fewer than 20 butterfly species ...
READ MORE

In this activity, students consider some of the ethical issues involved with keeping earthworms (and other animals) captive in a classroom setting. By the end of this activity, students should be ...
READ MORE

Pollinators are insects that visit flowers to drink nectar or feed on pollen. During this process, they get covered in pollen grains and then transport the pollen from one plant to another ...
READ MORE

In this activity, students use observation to explore earthworm anatomy and the nature of science. By the end of this activity, students should be able to: identify various physical ...
READ MORE

Although invisible to the naked eye, marine microbes drift continually in our ocean systems, quietly consuming up to 50% of the Earth’s CO2 through photosynthesis and producing nearly as much ...
READ MORE

iNaturalist logs hundreds of thousands of photos of flora, fauna and fungi. There are even sound recordings too. Each is described and geo located. iNaturalist is used by citizens and scientists ...
READ MORE

This New Zealand-based citizen science project collects data about butterflies in our gardens, schools, parks and farms – any location in the country or on the outer islands. This annual event – ...
READ MORE

To most of us, one earthworm resembles another. Although earthworms do have common characteristics, species differ widely in their size, skin colour and in the roles they play in the soil ...
READ MORE

Join Greta Dromgool and guest Giselle Clarkson in this recorded professional learning session which introduces the practice of observology. Giselle Clarkson is a New Zealand author and ...
READ MORE

This unit plan is designed for students in years 1–5. When someone mentions the word ‘butterfly’, what image pops into your head? Chances are it’s the monarch or the white butterfly, as these are ...
READ MORE
Dr Barbara Anderson, leader of Ahi Pepe MothNet, discusses the science protocols used in the project. One of the questions the project is trying to answer is whether vegetation restoration ...
READ MORE
Dr Robert Hoare, of Landcare Research NZ Ltd, takes us on a moth-collecting expedition. Join Dr Hoare as he goes out at night to collect moths for scientific study.
READ MORE
Dr Robert Hoare, of Manaaki Whenua – Landcare Research, talks about why he loves moths – a fascinating story of how an entomologist grew to love these night-time fliers. Points of interest ...
READ MORE

Exploring moths as ecological indicators of health and connectedness in our natural world. Select here for further information, transcript and copyright.
READ MORE

Learn more about introduced and native earthworms in Aotearoa New Zealand. Use the Slideshow menu for further options, including view full screen, and go here for the download option.
READ MORE
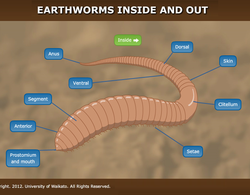
The earthworm’s body is well adapted for life in the soil. Click on the labels to see images and learn more. Select the green button to see what’s on the inside of an earthworm. Go here to view ...
READ MORE