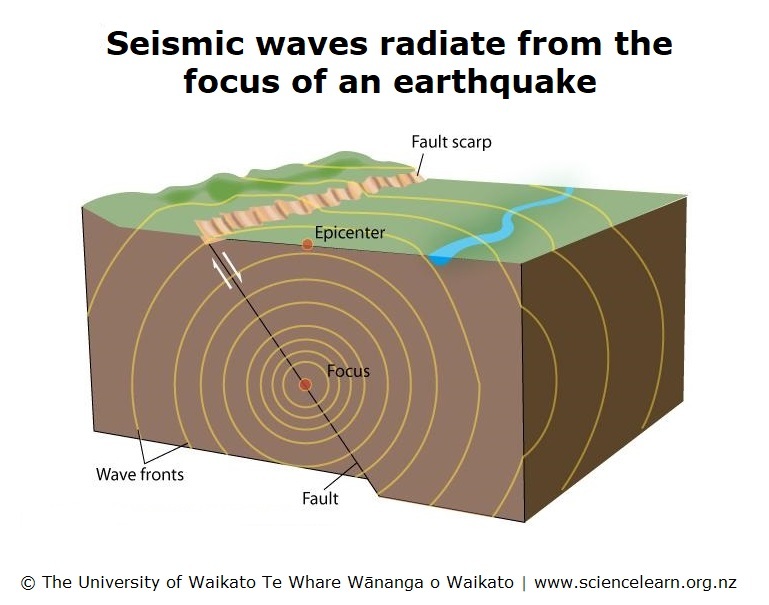
In this activity, students are introduced to some of the methods scientists use to record earthquakes. They obtain data from tables and graphs, carry out simple calculations and draw results on a map.
By the end of this activity, students should be able to:
- use seismograms from three recording stations to locate the epicentre of an earthquake
- measure the difference in arrival time of P-waves and S-waves, and read the distance from epicentre from a graph
- plot the epicentre location on a map
- investigate the area affected by the earthquake
- write a report that includes a prediction of possible damage, based on type of landscape, human and environmental features.
Download the Word file (see below) for:
- introduction/background
- what you need
- what to do
- student instructions
- seismograms from three North Island recording stations
- graph for calculating distance from epicentre
- outline map of North Island.
Related activity
Follow this activity with Earthquake intensity, where students allocate a Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) number to some historic New Zealand earthquakes and number to the area near the epicentre that they have just plotted.
Useful links
For records of recent and historic earthquakes go to the GeoNet website.
Acknowledgement
This activity was developed for the Earthquake Commission (EQC), now known as the Natural Hazards Commission, and has been kindly provided for use on the Science Learning Hub.