The periodic table of elements puts all the known elements into groups with similar properties. This makes it an important tool for chemists, nanotechnologists and other scientists. If you get to understand the periodic table, and learn to use it, you’ll be able to predict how chemicals will behave.
We’ll only cover the basics here, but it should be enough to start you off exploring the patterns and relationships to be found in the table.
Atoms
Atoms are the building blocks of matter. An atom has three basic parts – protons, neutrons and electrons. There are smaller particles, but they don’t concern us here. Protons and neutrons form the nucleus at the centre of an atom (hydrogen is a bit different, it only has a proton). Electrons move around within a large area of space outside the nucleus. The electrons are organised in energy levels – how an element behaves depends on how easy it is to gain or lose electrons in the outermost energy levels.
Atomic number
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons an atom has – the number of protons determines what an element is. For example, if an atom has six protons, it can only be carbon. The atomic number can also tell us how many electrons an atom has. From this, we can work out how the electrons are arranged, and this will tell us how an element will react with others.
Elements
An element is a substance that consists of atoms with the same atomic number. Elements cannot be split into simpler substances using normal chemical methods. The element iron is made only of iron atoms, and iron atoms are the same everywhere – iron atoms on Earth are the same as iron atoms on Mars.
The periodic table
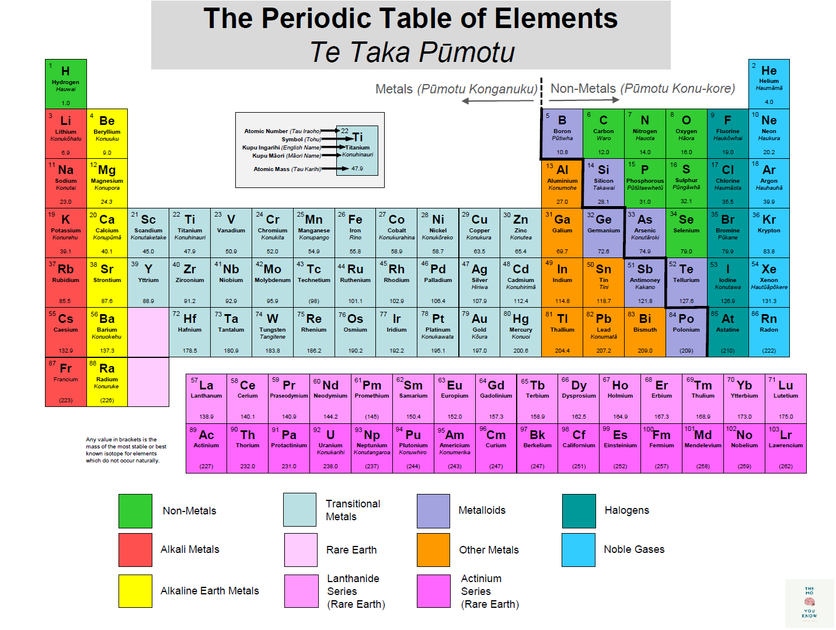
It will help to have a copy of the periodic table – the one here will get you started, or you can print a full one from the website below.
Each element has a square in the periodic table. In some versions of the table, these squares can contain a lot of writing, but to start with, three pieces of information are enough – each square should contain the name of the element, its official chemical symbol and its atomic number. For example, the square for iron will look a bit like this:
| 26 Fe Iron |
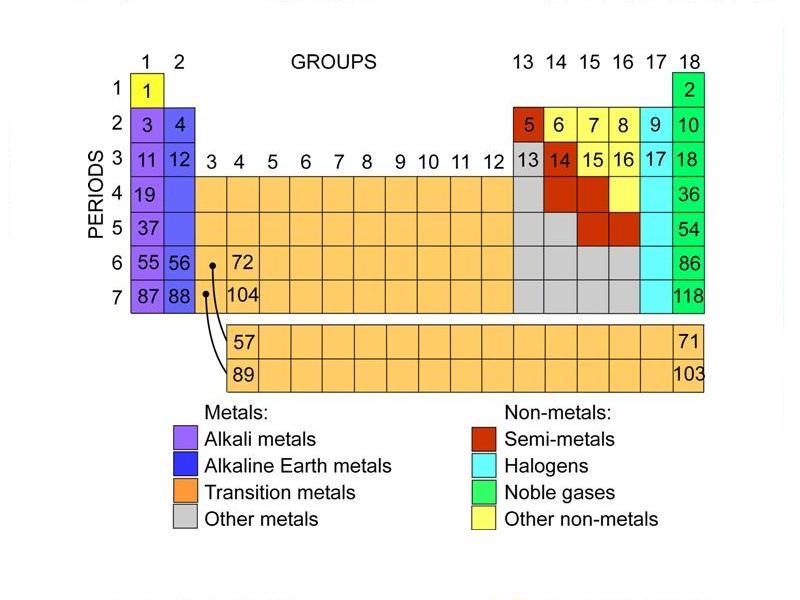
You’ll notice that elements in the periodic table are arranged in rows and columns.
- Rows are called periods.
- Columns are called groups.
Elements in a group (column) have the same number of outer electrons, so they have similar chemical properties.
There is an obvious pattern to look for:
- Atomic number increases as you move right along a row.
- Atomic number increases as you move down a column.
Other patterns are there, too, For example, the energy needed to get an electron away from an atom:
- goes up as you move left to right
- goes down as you move top to bottom
The more you find out about atomic structure, the more patterns and relationships you’ll find in the periodic table.
Group names
The groups of elements with similar properties have names and are normally coloured differently in a periodic table.
| Group 1 | Alkali metals. |
| Group 2 | Alkaline earth metals. |
| Groups 3–12 | Transition metals – Periodic tables have an extra block of transition metals at the bottom, for elements called rare-earths (or lanthanides) and actinides. The atomic numbers of these elements actually sit in the bottom left corner of the main table. |
| Groups 13–16 | Metals, semi-metals and non-metals – These share some properties, but not enough for a group to fill a column. |
| Group 17 | Halogens. |
| Group 18 | Noble gases. |
Hydrogen has the atomic number 1, so it sits at the top left of the table with the alkali metals of Group 1. It has the same number of electrons in its outermost energy level as the other elements in Group 1, but as it is a gas, it is normally put in the non-metal group.
Activity ideas
- Development of the periodic table – Use this article to find out about the first scientific discovery of an element in 1649 and how this grew into the periodic table as we know it today.
- Atomic clock – Use the atomic clock teacher resource to familiarise students with the names and symbols of the chemical elements.
- Element rap – In this activity, students become familiar with the names and symbols of the chemical elements by creating a rap or poem.
- Symbol find – In this activity, students become familiar with symbols of the chemical elements by creating them using letters from a phrase or sentence.
Related content
The Science Learning Hub team has curated a collection of resources related to the periodic table of elements. Login to make this collection part of your private collection, just click on the copy icon. You can then add additional content, notes and share and collaborate with others. Registering an account for the Science Learning Hubs is easy and free – sign up with your email address or Google account. Look for the Sign in button at the top of each page.
Useful links
Below are some websites devoted to the periodic table. They have interactive activities for students.
- www.teachengineering.org/activities/view/ucb-2791-periodic-table-intro-elements-activity
- https://ptable.com
- https://elements.wlonk.com/ElementsTable.htm
In 2019, the periodic table of elements observed its 150th anniversary. Radio New Zealand celebrated the International Year of The Periodic Table with the series Elemental.
Visit the International Year of the Periodic Table website.